Patient Consent for Electronic Health Information Exchange
Learn how health care providers can securely share and access health information through a health information exchange organization (HIE) with patient consent.
About Electronic Health Information Exchange (eHIE)
Electronic health information exchange (eHIE) — the way that health care providers share and access health information using their computers — is changing rapidly. One way some providers share and access information is through a third-party organization called a health information exchange organization (HIE).
HIEs help route information among various participating providers. In some HIEs, a provider can send out an electronic broadcast query that asks all provider participants whether they have information on a specific patient.
As eHIE increases, patient trust in HIEs must be ensured and patients may more often be asked to make a “consent decision.” This consent decision concerns the sharing and accessing of the patient’s health information through an HIE for treatment, payment, and health care operations purposes. When patients are asked to make consent decisions, we encourage providers, HIEs, and other health IT implementers to help patients make the consent decision meaningful.
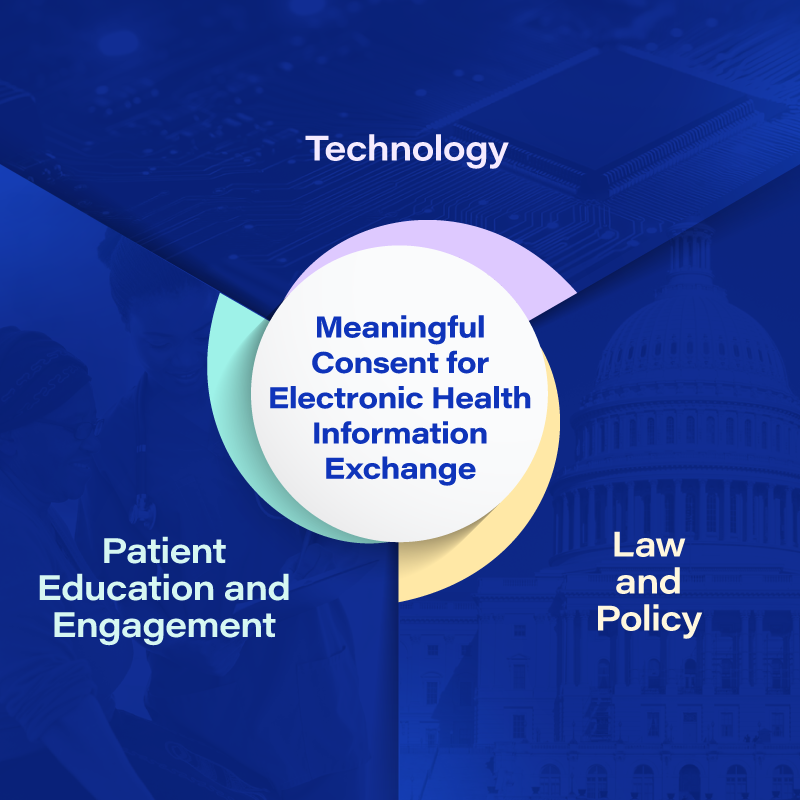
Implementers can enable meaningful consent by ensuring they consider the key parts displayed in the image to the right.
Meaningful Consent
What is meaningful consent?
Consent should not be a “check-the-box” exercise. Meaningful consent occurs when the patient makes an informed decision and the choice is properly recorded and maintained. Specifically, the meaningful consent decision has six aspects. The decision should be: made with full transparency and education, made only after the patient has had sufficient time to review educational material, commensurate with circumstances for why health information is exchanged (i.e., the further the information-sharing strays from a reasonable patient expectation, the more time and education is required for the patient before he or she makes a decision), not used for discriminatory purposes or as a condition for receiving medical treatment, consistent with patient expectations, and revocable at any time.
Enabling Privacy: Data Segmentation
Data segmentation refers to the electronic labeling or tagging of a patient’s health information in a way that allows patients or providers to electronically share parts, but not all, of a patient record. Data segmentation plays a crucial role in enabling privacy of patient records.